How To Delete Your Quibi Account
How To Delete Your Quibi Account. Click the gear icon in the top right corner of. Launch the app and tap the for you.
The relationship between a sign in its context and what it means is called"the theory on meaning. We will discuss this in the following article. we'll look at the difficulties with truth-conditional theories of meaning, Grice's examination of speaker-meaning, as well as The semantics of Truth proposed by Tarski. We will also discuss theories that contradict Tarski's theory about truth.
Arguments against truth-conditional theories of meaning
Truth-conditional theories of meaning claim that meaning is the result of the truth-conditions. However, this theory limits the meaning of linguistic phenomena to. The argument of Davidson is that truth-values may not be accurate. Therefore, we must be able to distinguish between truth and flat assertion.
Epistemic Determination Argument Epistemic Determination Argument is a method to establish truth-conditional theories for meaning. It is based on two fundamental foundational assumptions: omniscience over nonlinguistic facts, and knowing the truth-condition. However, Daniel Cohnitz has argued against these assumptions. So, his argument does not have any merit.
Another concern that people have with these theories is their implausibility of the concept of. However, this concern is dealt with by the mentalist approach. In this way, meaning can be examined in ways of an image of the mind, rather than the intended meaning. For example the same person may see different meanings for the one word when the person is using the same word in multiple contexts, however, the meanings for those words could be identical for a person who uses the same phrase in both contexts.
Though the vast majority of theories that are based on the foundation of definition attempt to explain significance in terms of mental content, other theories are occasionally pursued. This may be due to an aversion to mentalist theories. They can also be pushed with the view that mental representation needs to be examined in terms of linguistic representation.
Another significant defender of this viewpoint one of them is Robert Brandom. This philosopher believes that value of a sentence in its social context and that actions using a sentence are suitable in their context in the context in which they are utilized. This is why he has devised an argumentation theory of pragmatics that can explain sentence meanings using social practices and normative statuses.
Problems with Grice's analysis of speaker-meaning
Grice's analysis based on speaker-meaning puts significant emphasis on the utterer's intention and the relationship to the meaning to the meaning of the sentence. The author argues that intent is an abstract mental state that needs to be considered in order to grasp the meaning of an utterance. However, this approach violates speaker centrism through analyzing U-meaning without M-intentions. In addition, Grice fails to account for the possibility that M-intentions aren't limitless to one or two.
Additionally, Grice's analysis isn't able to take into account important cases of intuitional communication. For example, in the photograph example in the previous paragraph, the speaker doesn't make it clear whether he was referring to Bob and his wife. This is due to the fact that Andy's image doesn't clearly show whether Bob or wife is not faithful.
While Grice is right the speaker's meaning is more fundamental than sentence-meaning, there's some debate to be had. Actually, the distinction is essential to an understanding of the naturalistic validity of the non-natural meaning. Indeed, Grice's aim is to offer naturalistic explanations for the non-natural significance.
To understand a communicative act you must know the intent of the speaker, and that is a complex embedding of intentions and beliefs. However, we seldom make sophisticated inferences about mental states in simple exchanges. So, Grice's understanding of speaker-meaning isn't compatible with the actual processes that are involved in language comprehension.
Although Grice's explanation for speaker-meaning is a plausible explanation of this process it is only a fraction of the way to be complete. Others, like Bennett, Loar, and Schiffer, have developed more specific explanations. These explanations are likely to undermine the validity on the Gricean theory, since they consider communication to be a rational activity. It is true that people think that the speaker's intentions are valid because they perceive the speaker's motives.
In addition, it fails to account for all types of speech actions. Grice's analysis fails to include the fact speech acts are frequently used to explain the meaning of a sentence. This means that the value of a phrase is reduced to what the speaker is saying about it.
Problems with Tarski's semantic theory of truth
While Tarski believes that sentences are truth bearers, this doesn't mean that every sentence has to be true. Instead, he aimed to define what constitutes "true" in a specific context. His theory has become an integral part of contemporary logic, and is classified as correspondence or deflationary theory.
One of the problems with the theory of truth is that this theory is unable to be applied to a natural language. This is because of Tarski's undefinability theorem. It states that no language that is bivalent can be able to contain its own predicate. Although English might seem to be an the only exception to this rule This is not in contradiction with Tarski's view that all natural languages are closed semantically.
Yet, Tarski leaves many implicit constraints on his theory. For example, a theory must not contain false statements or instances of the form T. That is, the theory must be free of that Liar paradox. Another issue with Tarski's concept is that it is not conforming to the ideas of traditional philosophers. Furthermore, it's not able explain every single instance of truth in the ordinary sense. This is one of the major problems for any theories of truth.
The second issue is that Tarski's definition of truth calls for the use of concepts taken from syntax and set theory. These are not the best choices when looking at endless languages. Henkin's style in language is well founded, but it doesn't fit Tarski's definition of truth.
It is also problematic since it does not consider the complexity of the truth. Truth for instance cannot play the role of a predicate in the theory of interpretation, and Tarski's axioms do not be used to explain the language of primitives. Furthermore, the definition he gives of truth is not in line with the notion of truth in theory of meaning.
However, these concerns cannot stop Tarski using Tarski's definition of what is truth and it doesn't conform to the definition of'satisfaction. In fact, the proper definition of truth isn't so straight-forward and is determined by the specifics of object-language. If you're interested in learning more about it, read Thoralf Skolem's 1919 paper.
Problems with Grice's analysis of sentence-meaning
Grice's problems with his analysis of sentence meaning can be summed up in two main points. One, the intent of the speaker should be understood. Additionally, the speaker's speech must be supported by evidence that shows the intended effect. However, these criteria aren't being met in all cases.
The problem can be addressed through changing Grice's theory of meanings of sentences in order to take into account the significance of sentences that do not have intention. This analysis is also based upon the idea sentence meanings are complicated and contain a variety of fundamental elements. Accordingly, the Gricean analysis does not capture oppositional examples.
This argument is particularly problematic as it relates to Grice's distinctions of meaning of the speaker and sentence. This distinction is crucial to any account that is naturalistically accurate of sentence-meaning. This theory is also necessary in the theory of conversational implicature. As early as 1957 Grice proposed a starting point for a theoretical understanding of the meaning, which was elaborated in later publications. The principle idea behind the concept of meaning in Grice's research is to focus on the intention of the speaker in determining what the speaker wants to convey.
Another issue with Grice's method of analysis is that it does not take into account intuitive communication. For example, in Grice's example, it is not clear what Andy uses to say that Bob is unfaithful to his wife. However, there are a lot of cases of intuitive communications that are not explained by Grice's research.
The main premise of Grice's study is that the speaker must have the intention of provoking an emotion in the audience. This isn't intellectually rigorous. Grice sets the cutoff by relying on an individual's cognitive abilities of the speaker and the nature communication.
Grice's theory of sentence-meaning is not very credible, even though it's a plausible version. Others have provided more specific explanations of significance, but these are less plausible. In addition, Grice views communication as the activity of rationality. People reason about their beliefs through recognition of their speaker's motives.
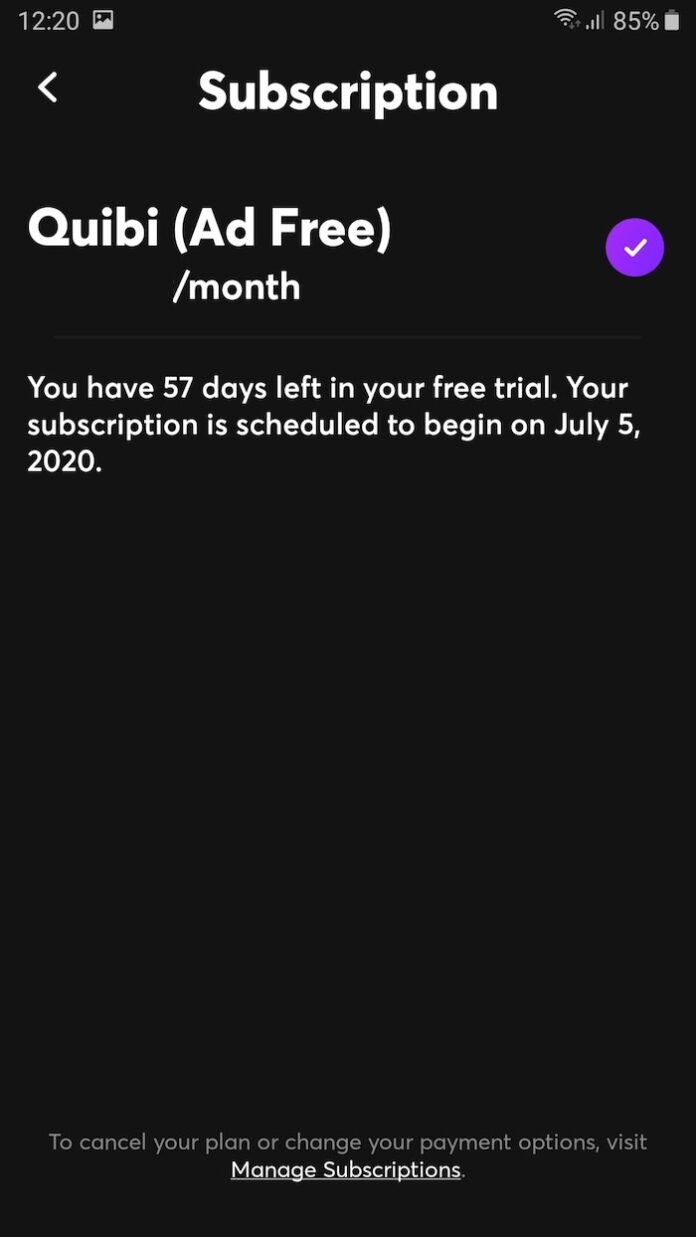
Among the options, tap on “my account”. On the next page, tap quibi > cancel and. Follow these instructions to stop recurring payments and/or delete your quibi:
To Cancel Quibi On Your Phone Simply:
Open the play store app. Launch the app and tap the for you. Among the options, tap on “my account”.
First Of All, On Your Ios Device, Open Up, “Settings”.
And then tap on your name to open a bunch of options on your screen. Subscriptions are either $4.99 or $7.99 per month, depending on if you decided. Follow these instructions to stop recurring payments and/or delete your quibi:
How To Cancel Your Quibi Subscription.
Click the gear icon in the top right corner of. Open the app on your device; The easiest way to save money as the quibi shut down looms is to unsubscribe from the app.
Click Here To Go To The Delete Account Page.
The easiest way to end your quibi subscription is from directly within the app itself. Open the side menu then tap “subscriptions.”. As previously announced, the quibi app as of tuesday (dec.
Next, Click On The “Subscriptions”.
Canceling in the quibi app. To remove an email account from gmail, follow these steps: On the delete account page, enter your account password.
Post a Comment for "How To Delete Your Quibi Account"