How Long Is Flight From Boston To Istanbul
How Long Is Flight From Boston To Istanbul. This assumes an average flight speed for a commercial airliner of 500 mph, which is equivalent to. How long is the flight time from boston to istanbul?
The relationship between a symbol in its context and what it means is called"the theory that explains meaning.. In this article, we will discuss the challenges of truth-conditional theories of meaning, Grice's study of speaker-meaning, as well as the semantic theories of Tarski. We will also look at the arguments that Tarski's theory of truth.
Arguments against truth-based theories of significance
Truth-conditional theories about meaning argue that meaning is a function of the conditions that determine truth. But, this theory restricts meaning to the phenomena of language. The argument of Davidson essentially states the truth of values is not always correct. In other words, we have to be able distinguish between truth-values and an assertion.
The Epistemic Determination Argument is a method to justify truth-conditional theories about meaning. It relies on two essential theories: omniscience regarding non-linguistic facts and the understanding of the truth-condition. However, Daniel Cohnitz has argued against these premises. This argument therefore has no merit.
Another issue that is frequently raised with these theories is the lack of a sense of the concept of. However, this concern is addressed by mentalist analysis. In this manner, meaning is analysed in ways of an image of the mind, rather than the intended meaning. For example someone could see different meanings for the same word if the same person uses the exact word in the context of two distinct contexts, however the meanings that are associated with these words may be identical as long as the person uses the same word in various contexts.
The majority of the theories of understanding of meaning seek to explain its how meaning is constructed in ways that are based on mental contents, other theories are occasionally pursued. This could be because of suspicion of mentalist theories. They also may be pursued by people who are of the opinion mental representation should be analysed in terms of linguistic representation.
A key defender of the view is Robert Brandom. He is a philosopher who believes that meaning of a sentence is dependent on its social setting in addition to the fact that speech events which involve sentences are appropriate in the situation in that they are employed. So, he's developed a pragmatics theory to explain the meaning of sentences by utilizing the normative social practice and normative status.
There are issues with Grice's interpretation of speaker-meaning
Grice's analysis based on speaker-meaning puts significant emphasis on the person who speaks's intention and the relationship to the significance of the phrase. He argues that intention is a mental state with multiple dimensions that needs to be understood in for the purpose of understanding the meaning of a sentence. However, this approach violates speaker centrism in that it analyzes U-meaning without considering M-intentions. Additionally, Grice fails to account for the reality that M-intentions can be restricted to just one or two.
Furthermore, Grice's theory doesn't take into consideration some essential instances of intuition-based communication. For instance, in the photograph example from earlier, the person speaking doesn't clarify if he was referring to Bob or to his wife. This is problematic because Andy's photograph doesn't indicate the fact that Bob as well as his spouse is unfaithful , or loyal.
While Grice believes the speaker's meaning is more fundamental than sentence-meaning, there's still room for debate. In actual fact, this distinction is essential for the naturalistic reliability of non-natural meaning. Indeed, the purpose of Grice's work is to offer an explanation that is naturalistic for this non-natural meaning.
To appreciate a gesture of communication we must first understand what the speaker is trying to convey, and that is an intricate embedding and beliefs. Yet, we rarely make complex inferences about mental states in typical exchanges. This is why Grice's study of meaning-of-the-speaker is not in accordance with the actual processes that are involved in language understanding.
While Grice's account of speaker-meaning is a plausible explanation to explain the mechanism, it's only a fraction of the way to be complete. Others, such as Bennett, Loar, and Schiffer have come up with deeper explanations. These explanations, however, make it difficult to believe the validity in the Gricean theory, because they view communication as an act of rationality. It is true that people accept what the speaker is saying as they can discern their speaker's motivations.
Additionally, it fails to reflect all varieties of speech act. The analysis of Grice fails to account for the fact that speech acts can be employed to explain the significance of sentences. This means that the meaning of a sentence can be reduced to the speaker's interpretation.
Issues with Tarski's semantic theory of truth
While Tarski said that sentences are truth-bearing However, this doesn't mean any sentence is always truthful. Instead, he aimed to define what is "true" in a specific context. His theory has since become an integral part of modern logic and is classified as deflationary or correspondence theory.
One problem with the theory of the truthful is that it can't be applied to any natural language. This problem is caused by Tarski's undefinability concept, which claims that no bivalent one could contain its own predicate. Even though English may seem to be an a case-in-point and this may be the case, it does not contradict the view of Tarski that natural languages are closed semantically.
But, Tarski leaves many implicit conditions on his theory. For example the theory should not contain false statements or instances of the form T. This means that it is necessary to avoid it being subject to the Liar paradox. Another drawback with Tarski's theory is that it's not as logical as the work of traditional philosophers. It is also unable to explain every aspect of truth in terms of ordinary sense. This is an issue for any theory of truth.
Another issue is that Tarski's definition for truth demands the use of concepts of set theory and syntax. These are not appropriate when looking at endless languages. Henkin's language style is well founded, but it does not fit with Tarski's notion of truth.
This definition by the philosopher Tarski unsatisfactory because it does not make sense of the complexity of the truth. For instance, truth can't be predicate in an analysis of meaning, and Tarski's definition of truth cannot clarify the meaning of primitives. Additionally, his definition of truth is not in line with the concept of truth in theory of meaning.
However, these issues will not prevent Tarski from applying the definitions of his truth and it does not conform to the definition of'satisfaction. Actually, the actual definition of truth is less straight-forward and is determined by the peculiarities of language objects. If you want to know more about the subject, then read Thoralf Skolem's 1919 article.
A few issues with Grice's analysis on sentence-meaning
The difficulties with Grice's interpretation of sentence meaning can be summarized in two main areas. First, the intentions of the speaker has to be recognized. The speaker's words is to be supported by evidence that shows the intended outcome. But these conditions are not observed in all cases.
The problem can be addressed by changing Grice's analysis of meaning of sentences, to encompass the meaning of sentences that do not have intention. This analysis is also based on the premise that sentences are highly complex entities that have several basic elements. So, the Gricean analysis fails to recognize instances that could be counterexamples.
This critique is especially problematic with regard to Grice's distinctions between meaning of the speaker and sentence. This distinction is fundamental to any plausible naturalist account of the meaning of a sentence. This theory is also crucial for the concept of implicature in conversation. When he was first published in the year 1957 Grice proposed a starting point for a theoretical understanding of the meaning, which he elaborated in subsequent papers. The basic concept of significance in Grice's research is to look at the speaker's motives in determining what the speaker intends to convey.
Another problem with Grice's study is that it does not account for intuitive communication. For example, in Grice's example, there is no clear understanding of what Andy means by saying that Bob is not faithful for his wife. However, there are plenty of variations of intuitive communication which do not fit into Grice's explanation.
The main premise of Grice's model is that a speaker must be aiming to trigger an emotion in people. However, this assumption is not scientifically rigorous. Grice determines the cutoff point in relation to the possible cognitive capabilities of the interlocutor and the nature of communication.
Grice's sentence-meaning analysis doesn't seem very convincing, although it's a plausible version. Different researchers have produced more elaborate explanations of significance, but these are less plausible. Furthermore, Grice views communication as the activity of rationality. Audiences reason to their beliefs through their awareness of communication's purpose.
How far is istanbul from boston? This assumes an average flight speed for a commercial airliner of 500 mph, which is equivalent to. You can travel there, but you'll have to quarantine on your return.
How Long Is The Boston To Istanbul Flight Time & Schedule.
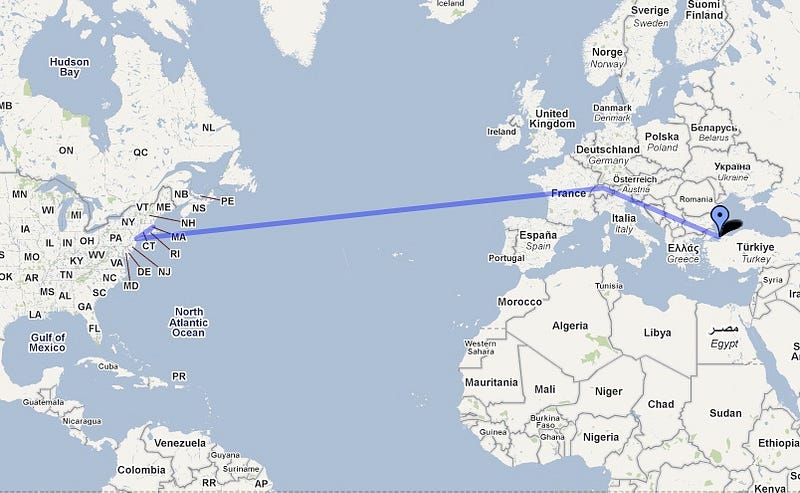
The total flight duration from boston, ma to istanbul, turkey is 10 hours, 10 minutes. Flight time from boston to istanbul. How long does it take to fly from boston logan international to istanbul?
4,836 Miles Or 7782 Km Flight Time:
The cheapest flight from boston to istanbul airport was found 71 days before departure, on average. How long is the flight time from boston to istanbul? The flight time is approximately 9 hours 53 minutes.
Interesting Facts About Flights From Boston To Istanbul (Bos To Saw) What Airlines Fly Direct From Bos Airport To Saw Airport?
Here's the quick answer if you have a private jet and you can fly in the fastest possible straight line. Here's the quick answer if you have a private jet and you can fly in the fastest possible straight line. 9 hours and 24 minutes is the average flight time from boston logan international to istanbul.
How Long Does It Take To Fly From Boston To Istanbul?
How far is boston from istanbul? The initial bearing on the course from boston to istanbul is 91.03° and the compass direction is e. How far is istanbul from boston?
Istanbul Currently Has Moderate Travel Restrictions For Travellers From Boston.
Browse departure times and stay updated with the latest flight schedules. How long is the flight time from boston to istanbul &. The earliest flight departs at.
Post a Comment for "How Long Is Flight From Boston To Istanbul"